Tropical Rainforest Plants Adaptations To Environment
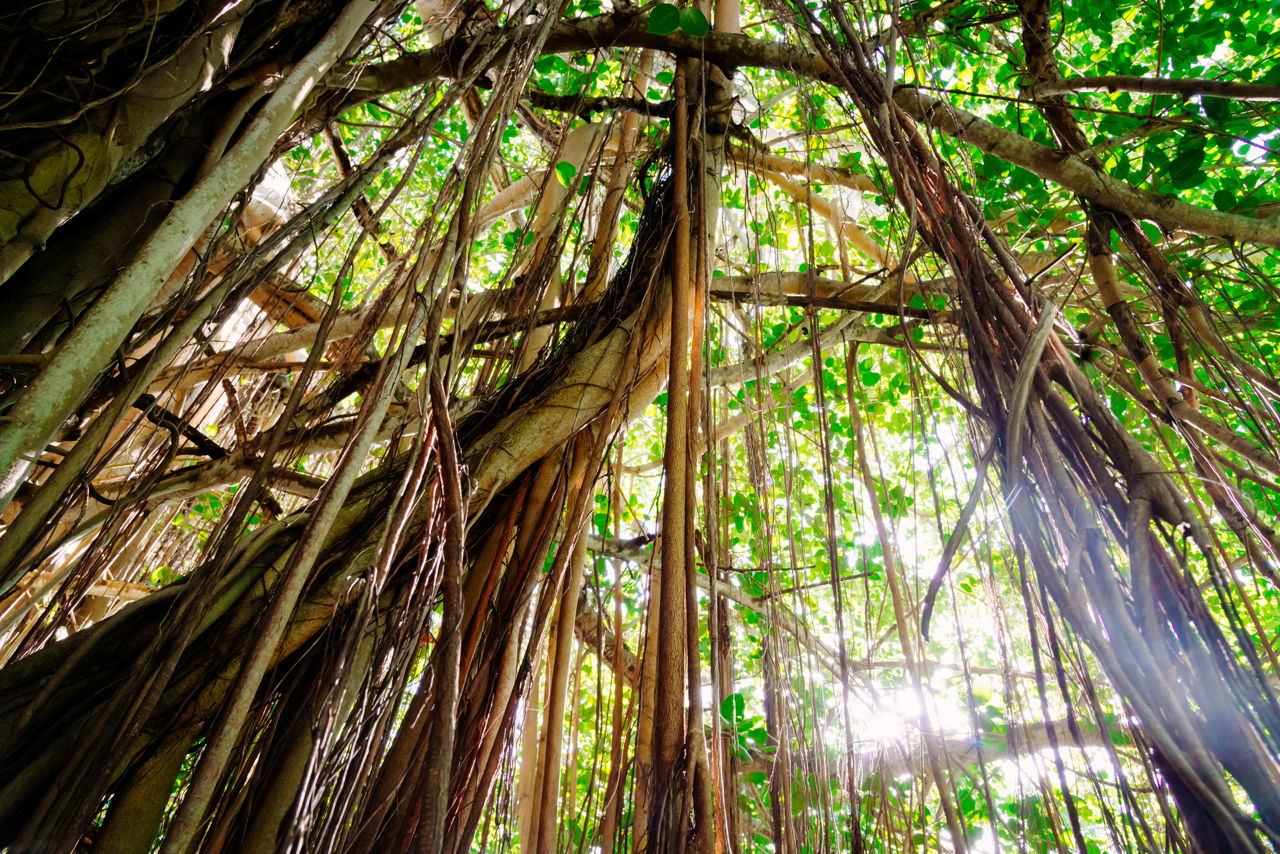

The smoothness of the bark may also make it difficult for other plants to grow on their surface.
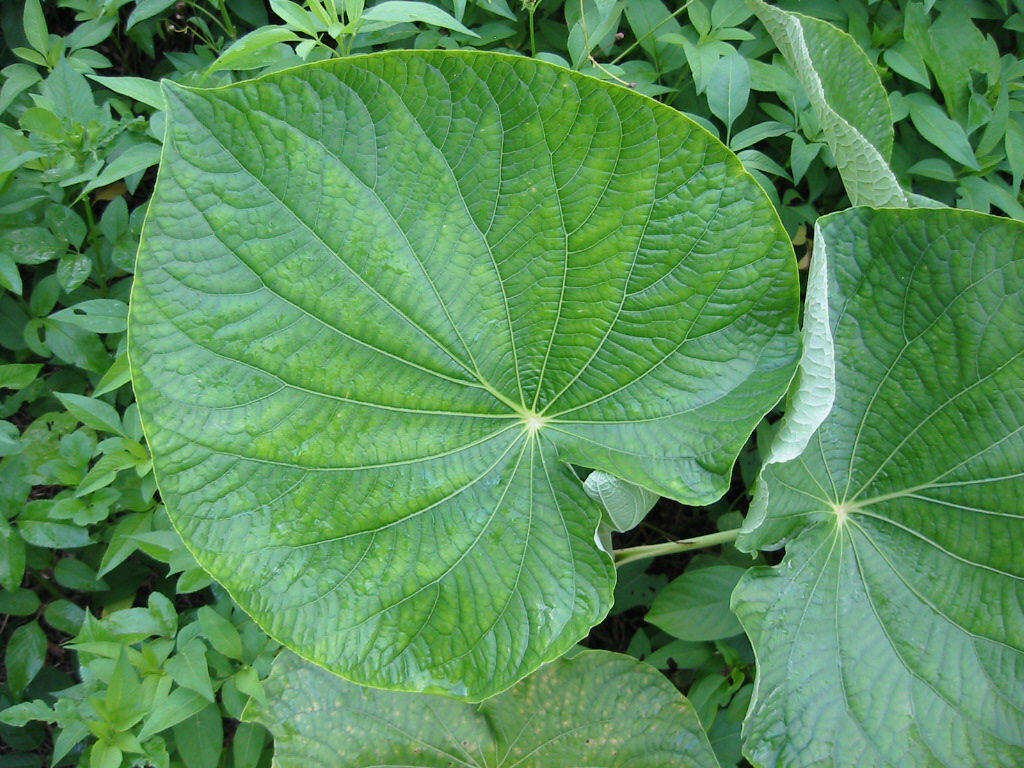
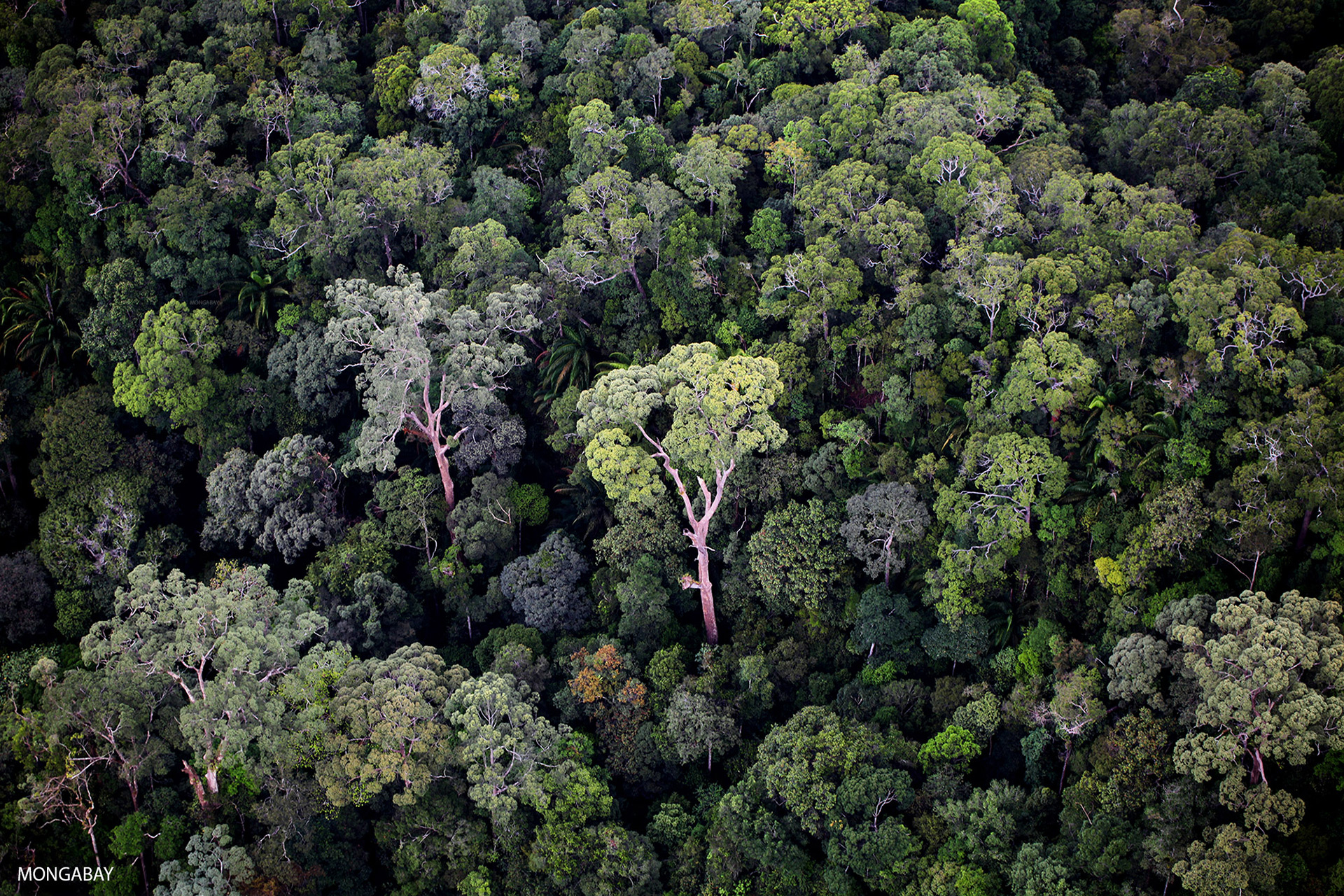
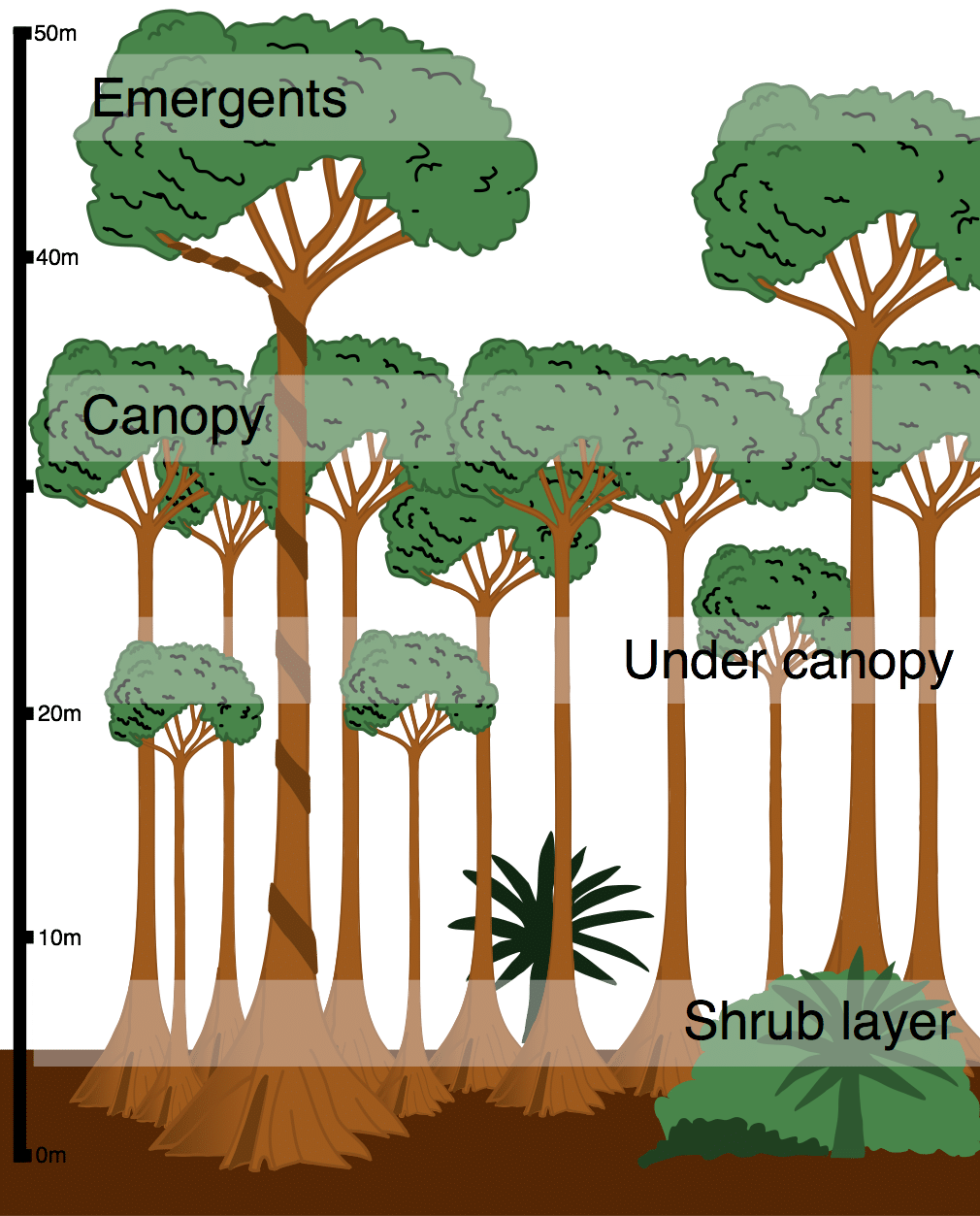
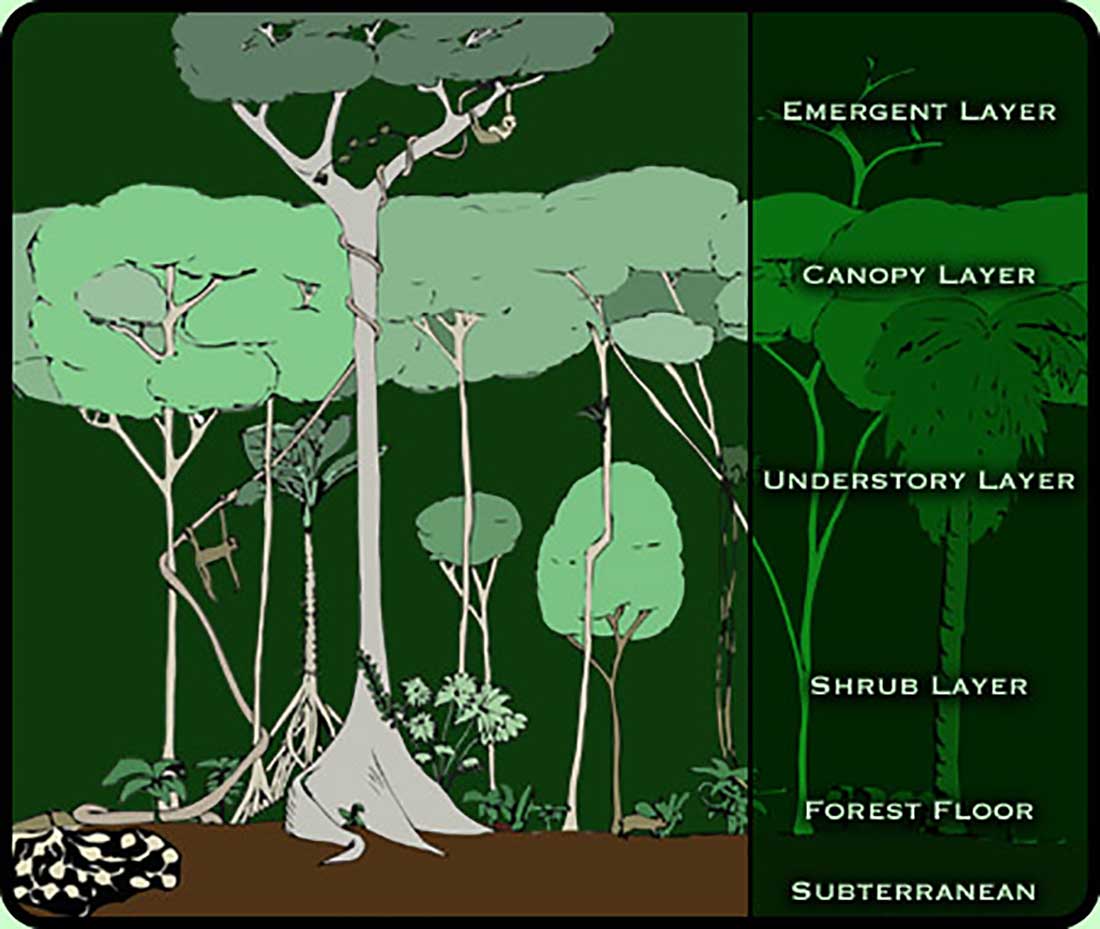
Tropical rainforest plants adaptations to environment. Their leaves and flowers grow in the canopy. In order to get the sunlight that they need plants have to be able to grow faster or to have bigger leaves than their neighbours. Rainforest plants and animals have developed adaptations that help them to thrive.
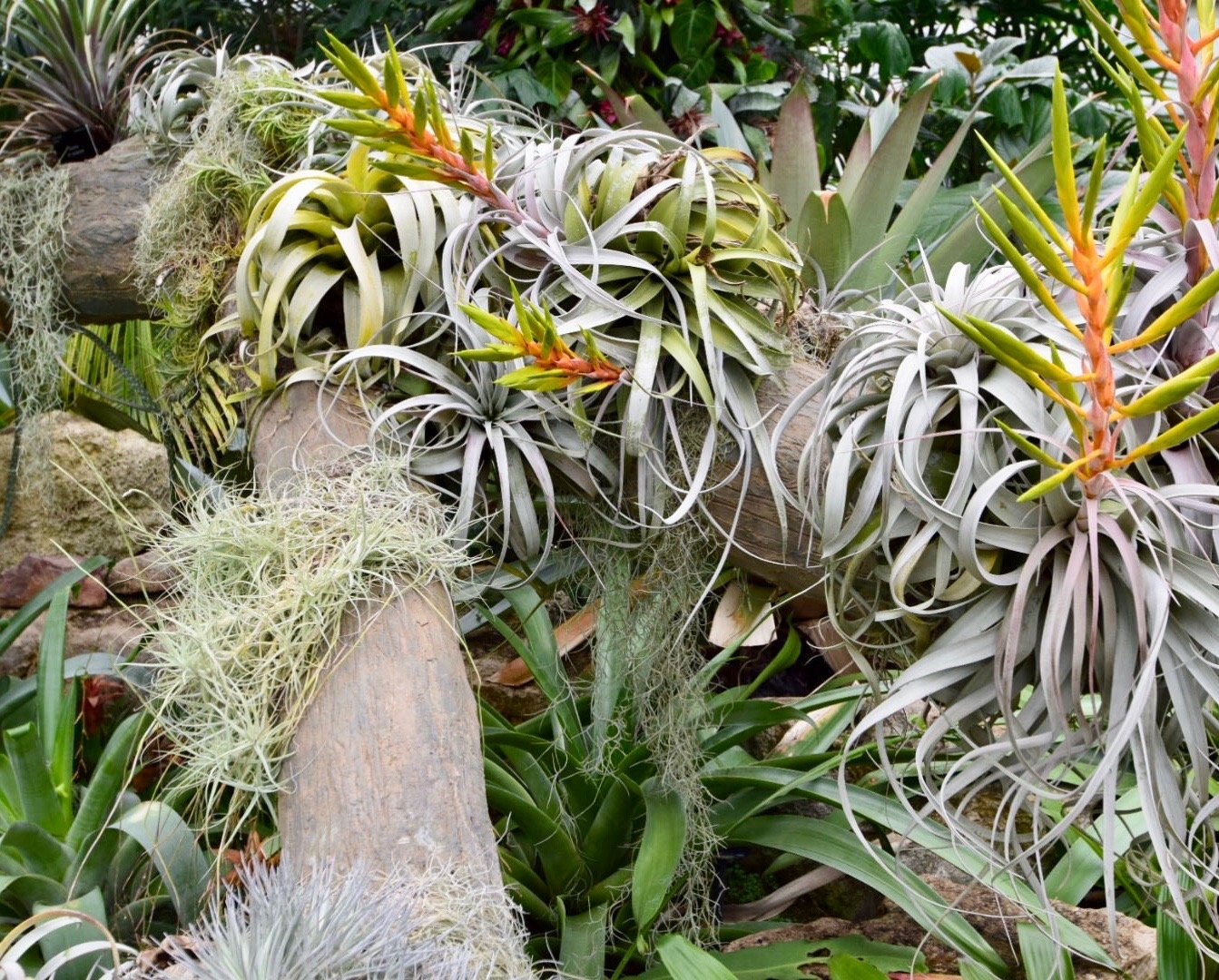
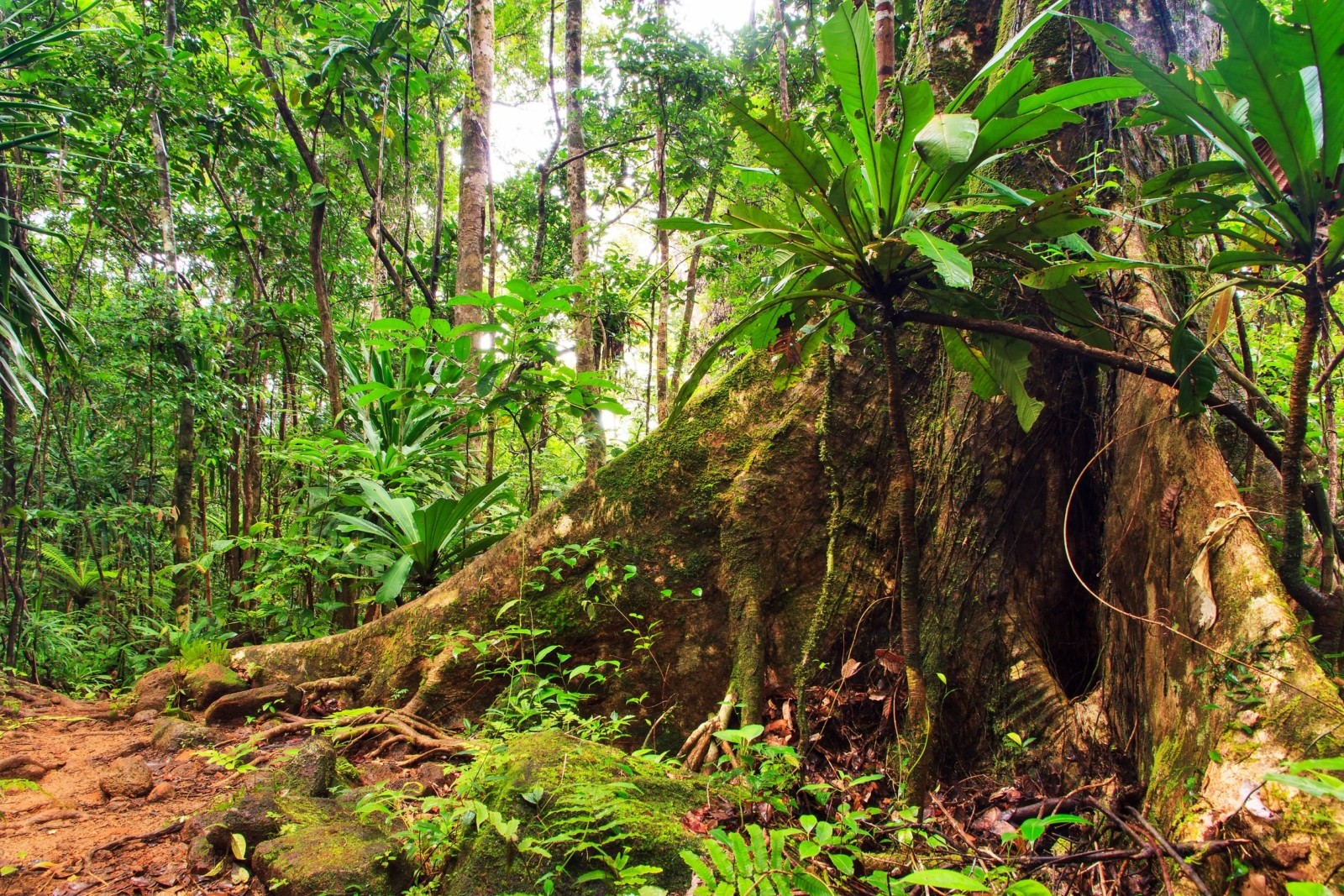
Most plants in the tropical rainforest have adapted to the strong sunlight heavy rain thin soils and dark conditions in the undergrowth. Bark In drier temperate deciduous forests a thick bark helps to limit moisture evaporation from the trees trunk. A few examples of tropical rainforest plants are Avocado Trees Orchids Ferns Bromeliads Banana Trees Rubber Trees Bamboo Trees Cacao etc.
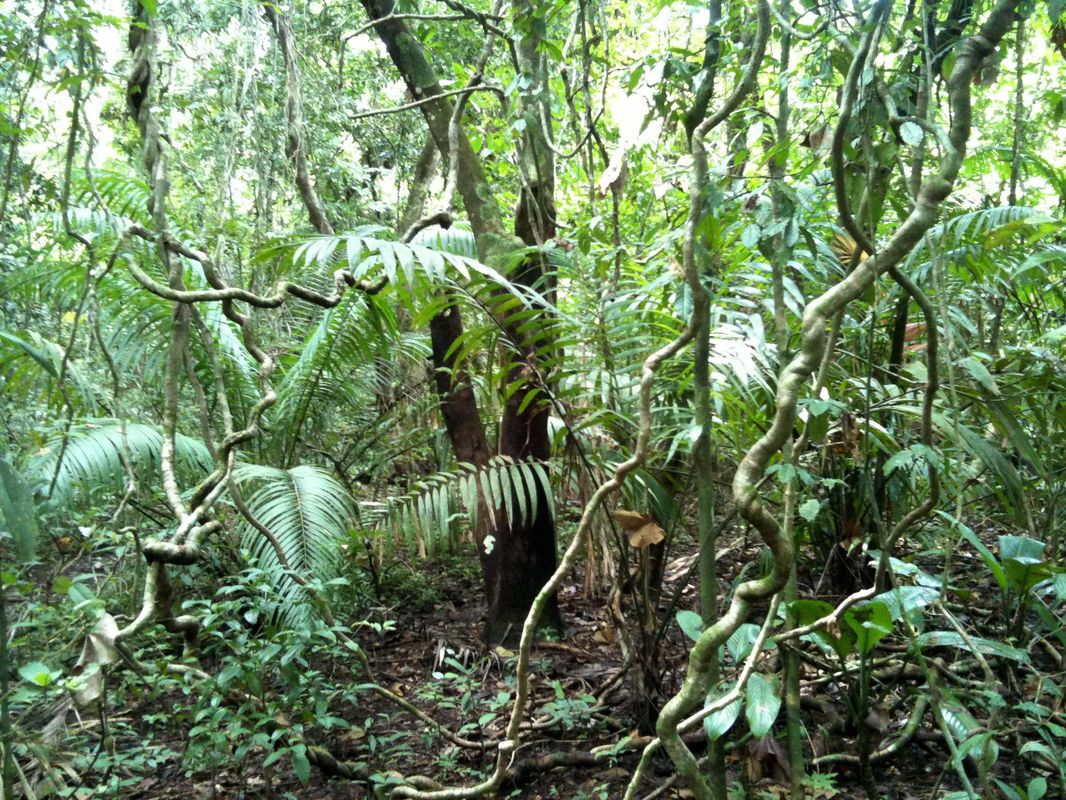
Plant Adaptations in the Tropical Rainforest Biome. Lianas - these are woody vines that have roots in the ground but climb up the trees to reach the sunlight. Tropical rainforest trees generally have thin bark.
The tropical rainforest environment is characterized by high temperatures and an abundance of rainfall leading to high levels of humidity. Vegetation in the tropical rainforest has adapted to thrive in its hot wet climate in a range of ways. Many animals are able to camouflage to avoid predators.
Tropical rainforest flora have to adapt to an environment that is always hot and wet. Plants and animals living in the Tropical Rainforest must be able to adapt to the year round humidity and constant warm humid and wet weather. Most trees in these tropical regions have straight trunks with no branches or leaves until they reach the canopy layer.
The leaves of forest trees have adapted to cope with exceptionally high rainfall. Also some leaves have flexible stems so they can turn toward the sun another adaptation is. Some rainforest trees have special characteristics which are signs of adaptation to their environment.