Production Of Transgenic Animals Notes
Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture 2018.
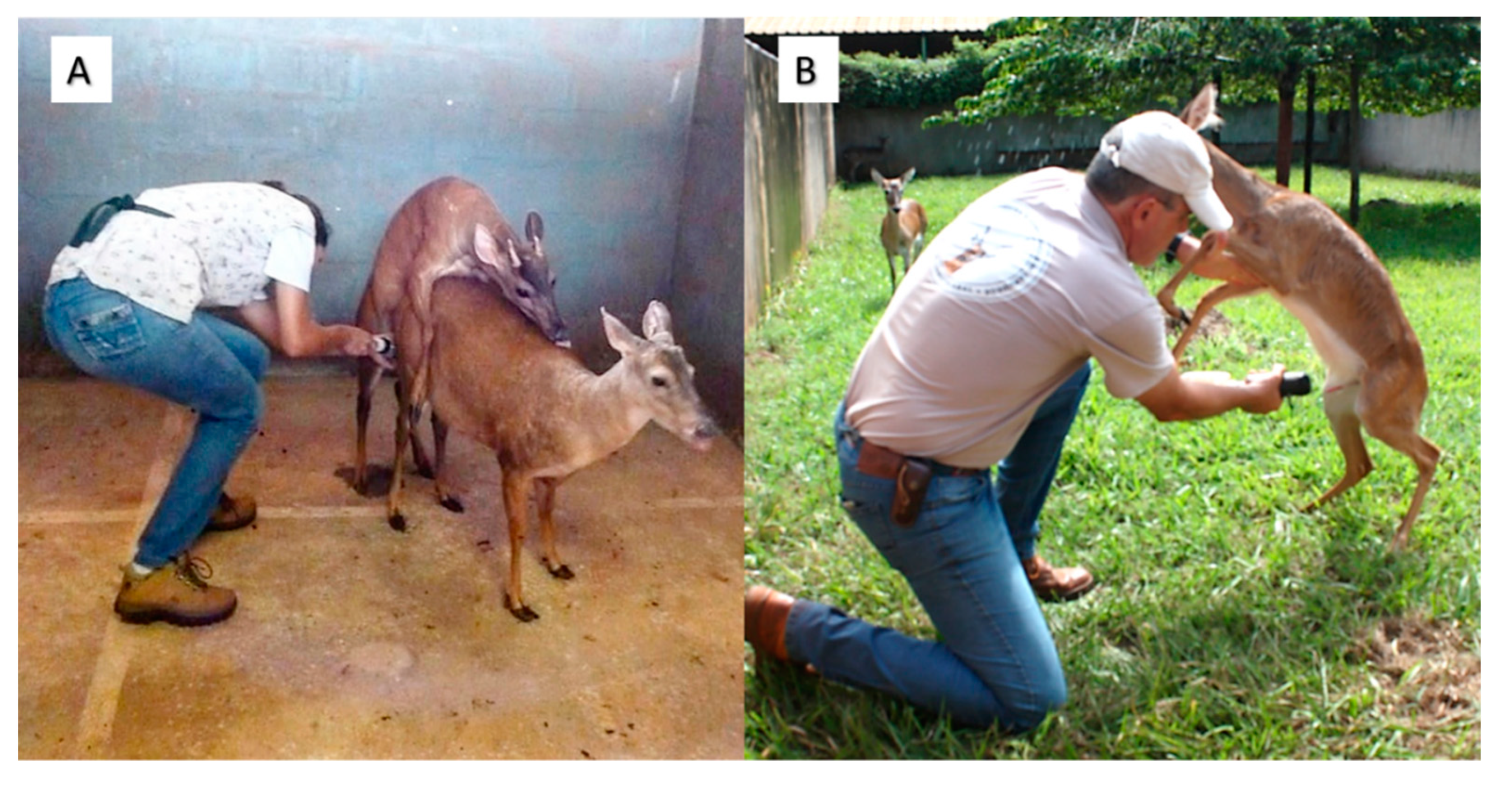
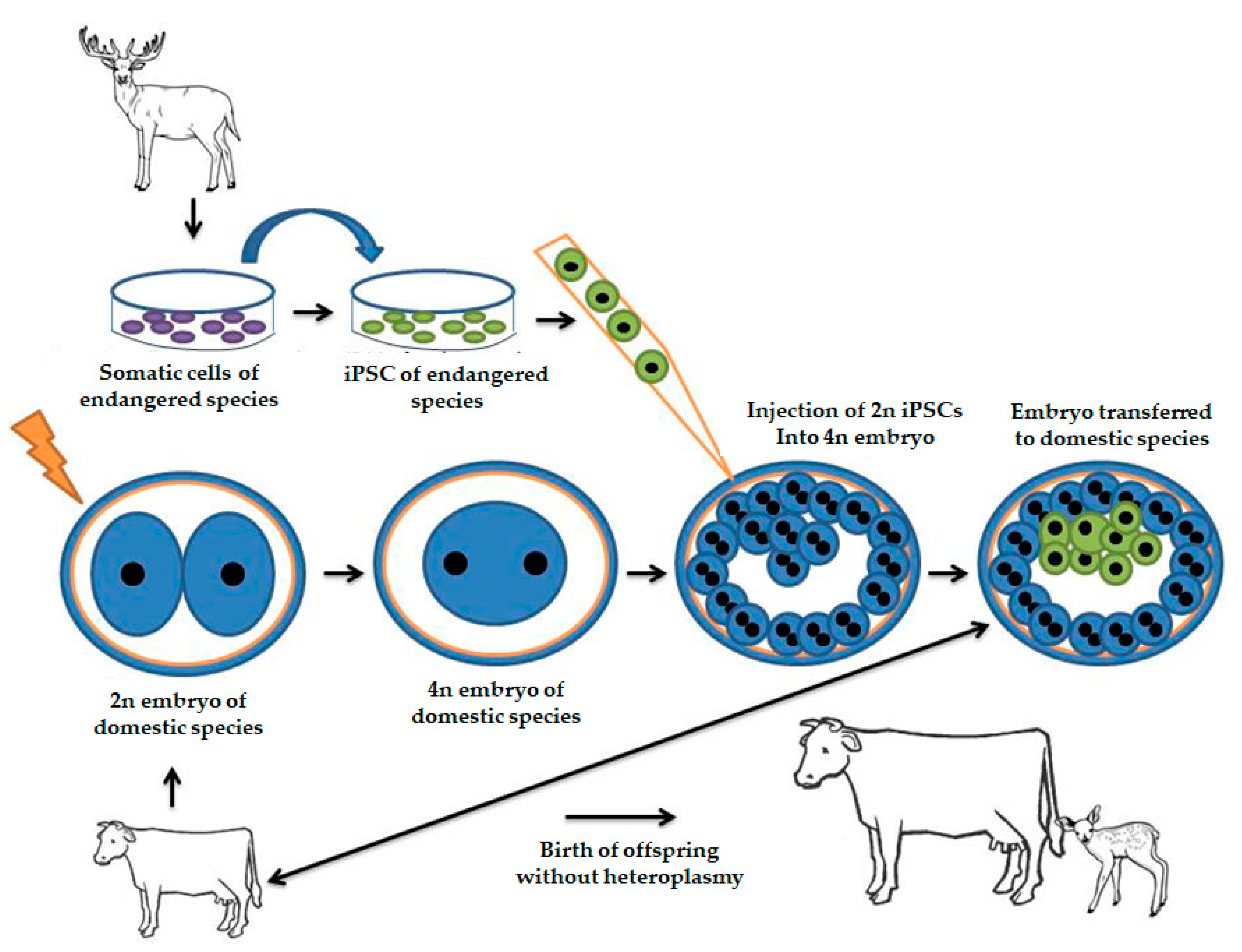
Production of transgenic animals notes. A transgenic animal is an animal in which one or more genes have been introduced into its nonreproductive cells. The cells are then incorporated into an embryo at the blastocyst stage of development. Applications of Genetically modified animals.
The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it to be incorporated into the DNA of the host and to be expressed correctly by the cells of the host. The first transgenic animal was produced is mice by injecting DNA to mouse embryos then implanting the embryos in female mice.
Transgenic mice are developed by injecting DNA into the oocytes or 1-2 celled embryos taken from female mice. Due to the controversial concept of cloning and scientific testing on animals there are many questions that revolve around this topic. Transgene is incorporated into the ES cell by Microinjection By a retro virus By electroporation Transgenic stem cells are grown in vitro.
Transgenic animals can be used to produce valuable products. ES cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. Advantages of Transgenic Animals.
The medical and biotechnological uses of animal cloning are almost innumerable as many diseases have been eradicated thanks to the production of these transgenic animals. Transgenic animals are used as tools in research and for the production of recombinant proteins The main applications of transgenic animals are described as follows. Benefits of Transgenic Animals The benefits of these animals to human welfare can be grouped into areas.
The first transgenic animal was produced in 1983 when genes for human growth hormone were introduced into mice. One favoured method involves the inoculation of the DNA into the pronucleus of a fertilised ovum followed by implantation into pseudo pregnant females. Studying gene function.