Desert Animals Adaptations To Conserve Water

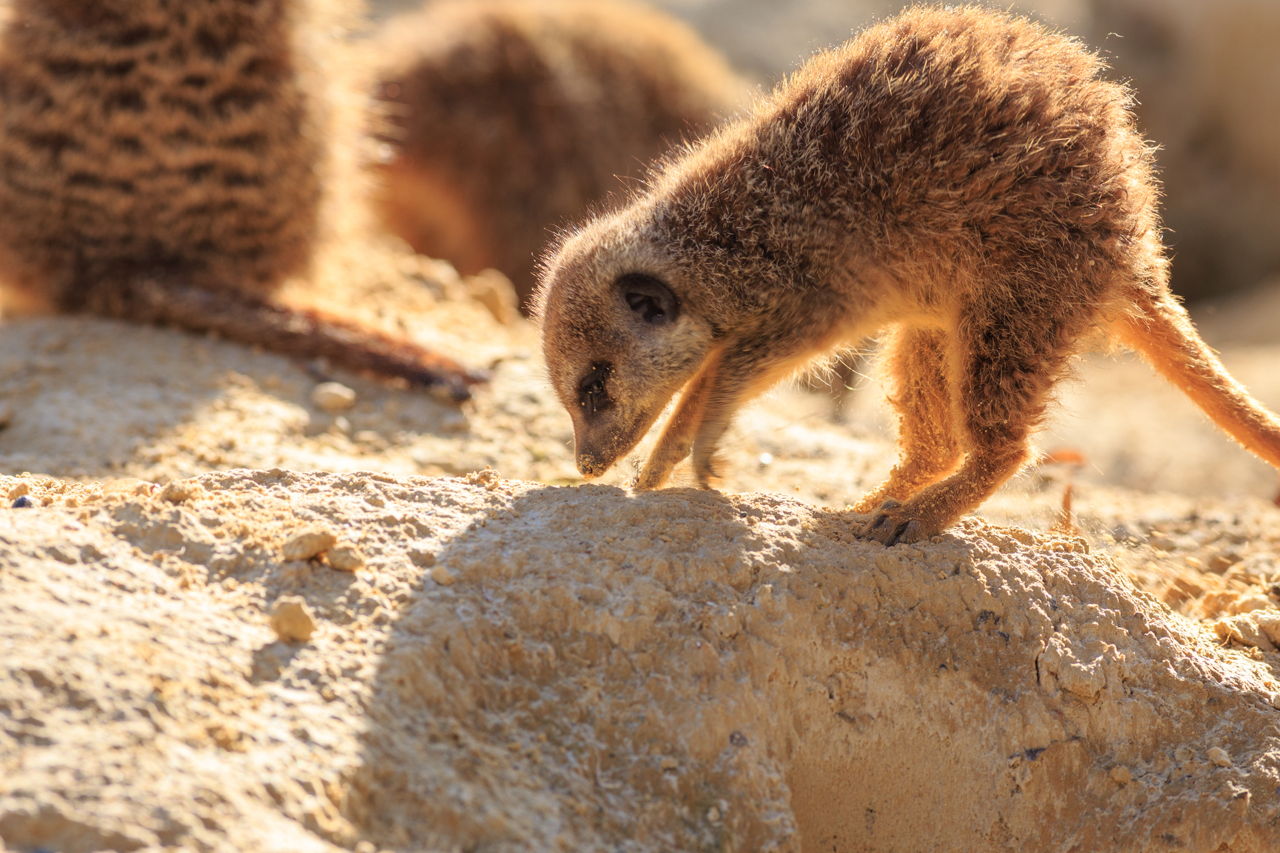
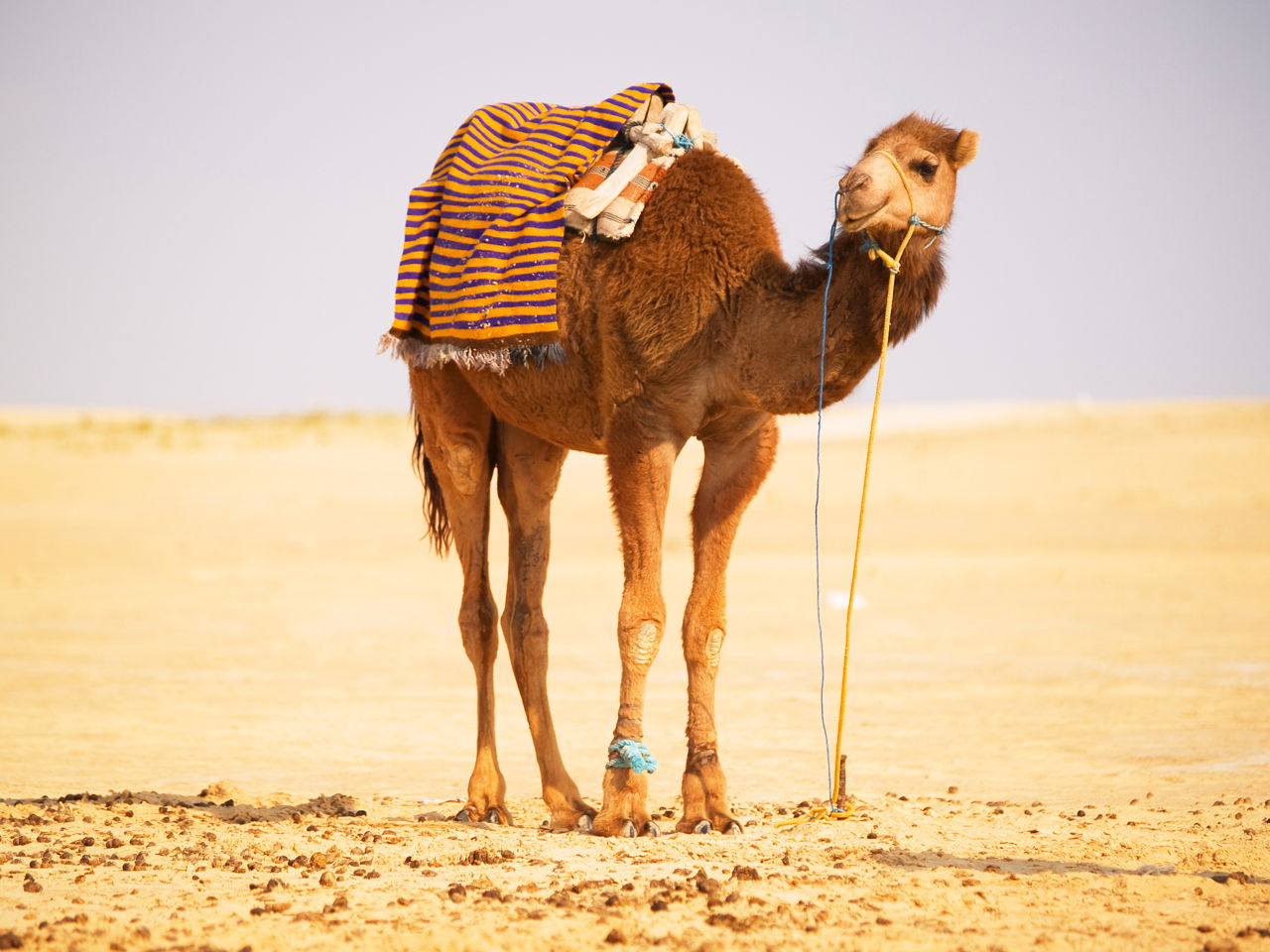
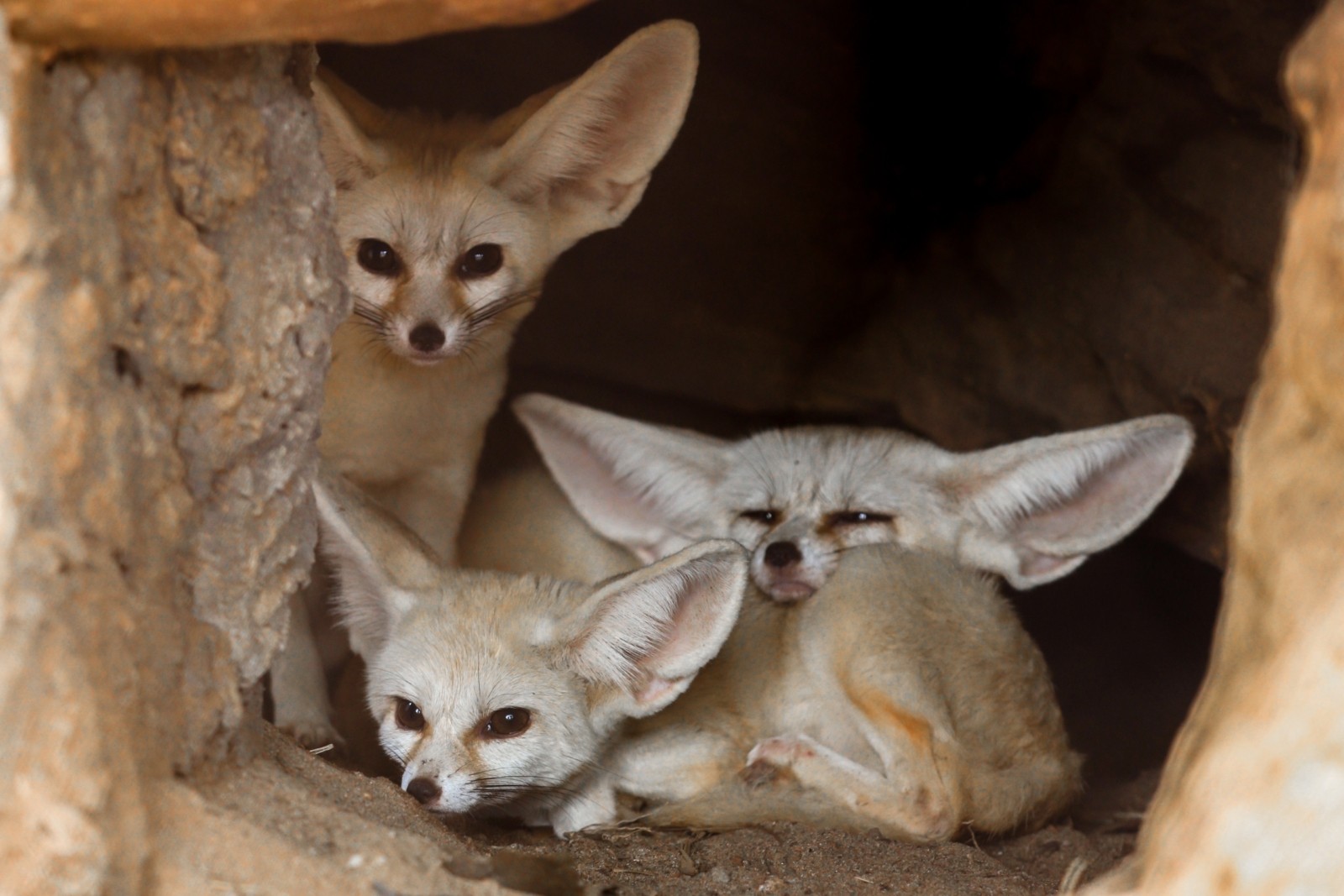
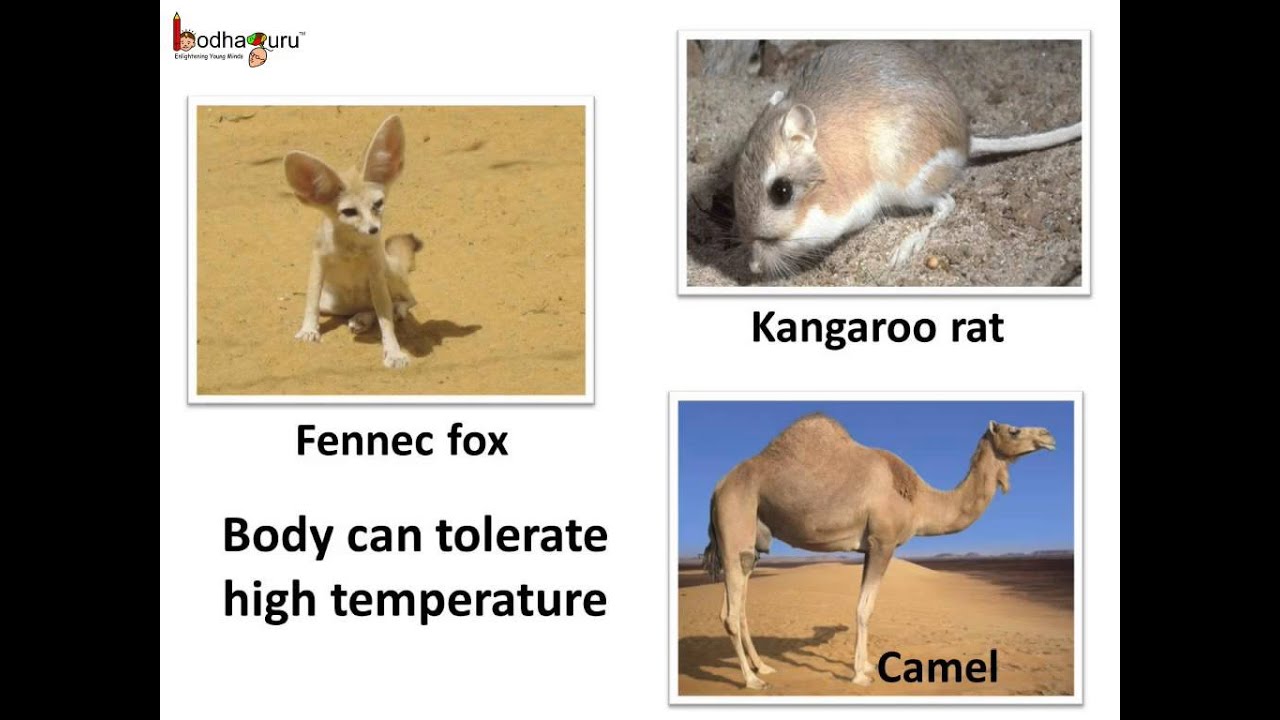
Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water.
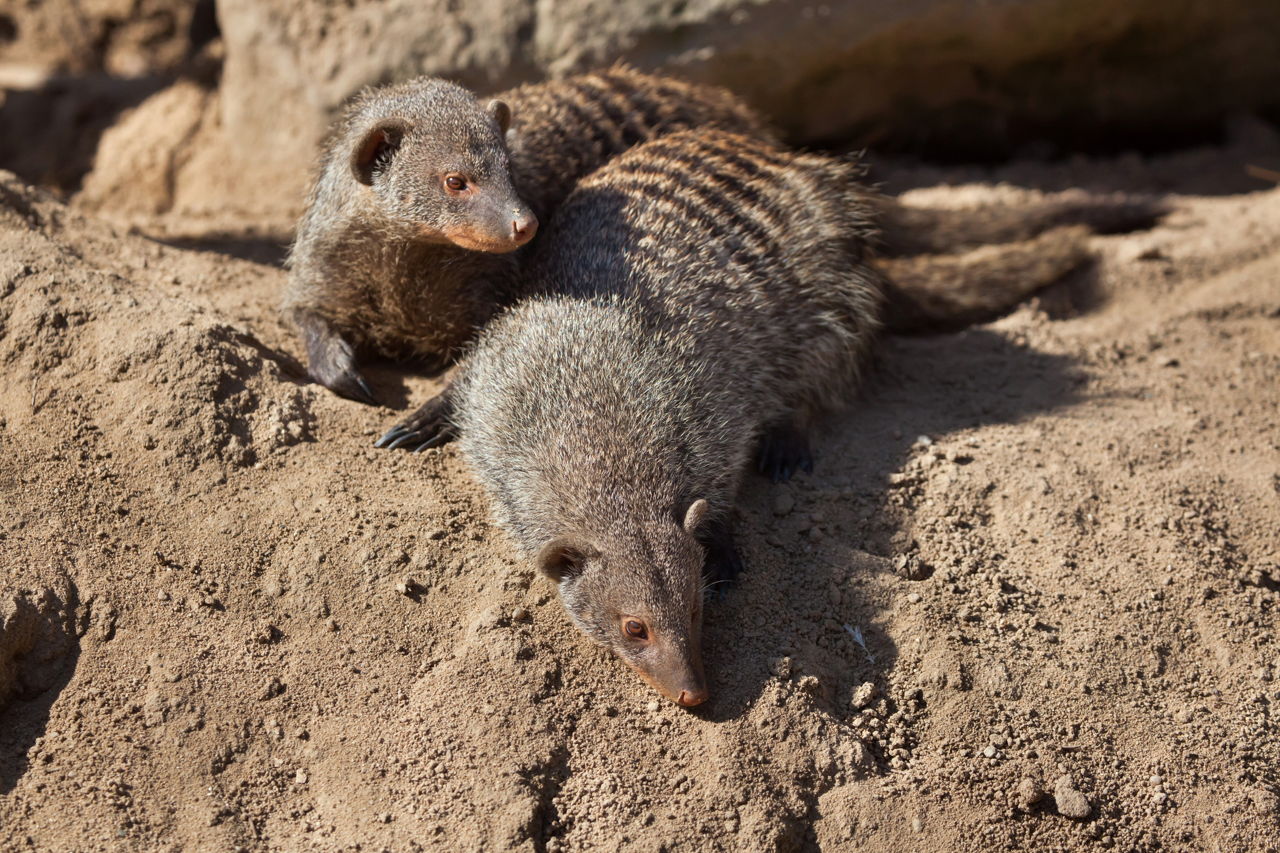
Desert animals adaptations to conserve water. Succulent plants seeds or the blood and body tissues of their prey. Nocturnal animals avoid activity during the. The most animals small size use these strategies to adapt to the desert.
One of the biggest water retention adaptations desert animals have is simply to avoid the sun and extreme heat. In areas with a greater water supply the level of biodiversity increases as vegetation such as shrubs cacti and hardy trees. Adaptations of Desert Plants.
Plants in deserts have adaptations to conserve water. Which animal is a classic example of adaptation to the desert conditions. Few animals have adapted to survive the hottest desert regions besides scorpions and small reptiles.
Extreme desert is without any vegetation and rainfall. To conserve water they avoid evaporation and concentrate excretions ie. Among the thousands of desert animal species there are almost as many remarkable behavioral and structural adaptations developed for avoiding excess heat.
Camels arent the only animals that. Equally ingenious are the diverse mechanisms various animal species have developed to acquire conserve. For example cacti have enlarged stems to store water as well as spines to protect these water reserves from thirsty animals.
All desert animals have learned ways and have adapted themselves either voluntarily or involuntarily to avoid the heat of the desert by simply staying out of it as much as possible. Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water. Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water.