Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

Seep communities are more dispersed in areas where hydrocarbons particularly methane or other natural gases are percolating up through deep-sea sediments.
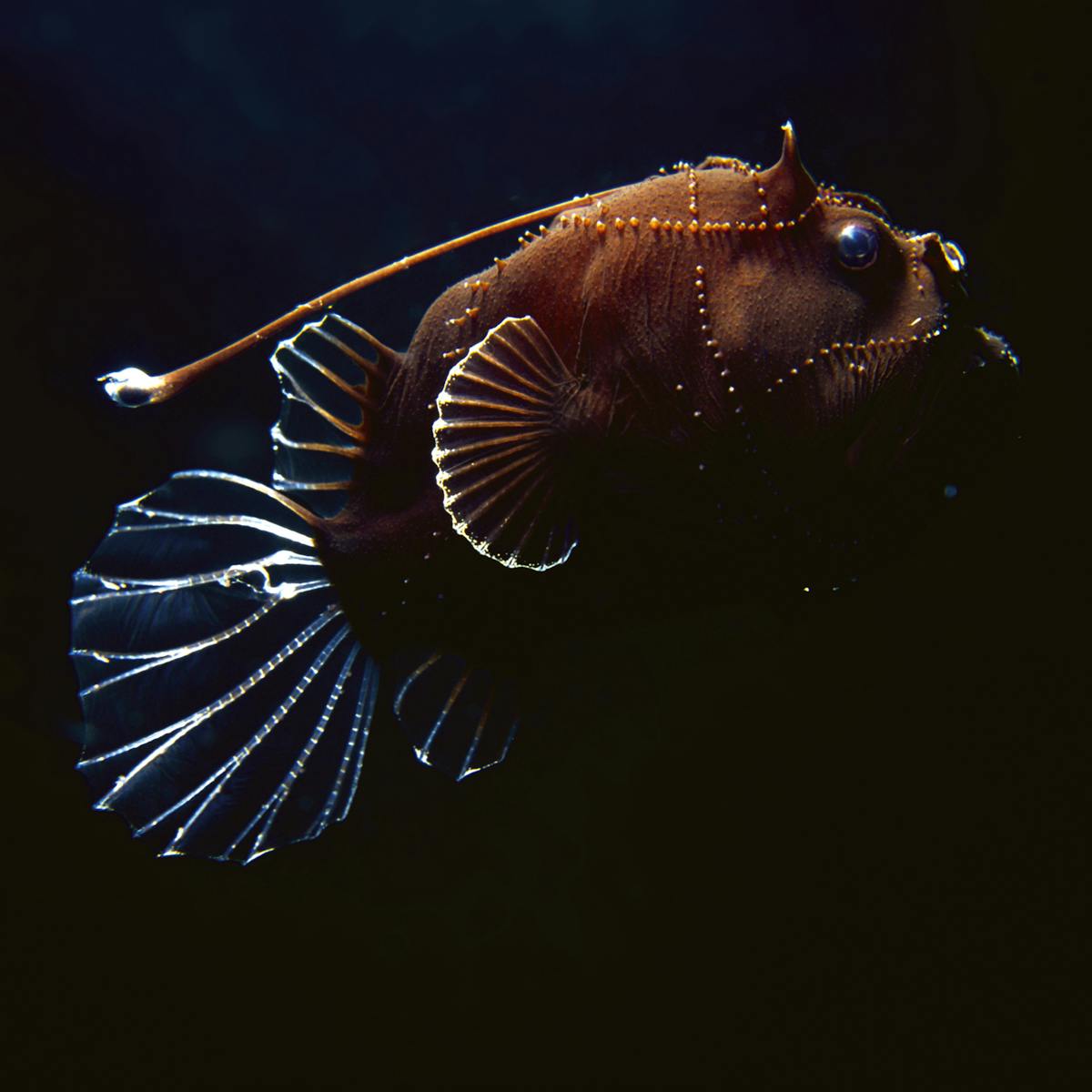
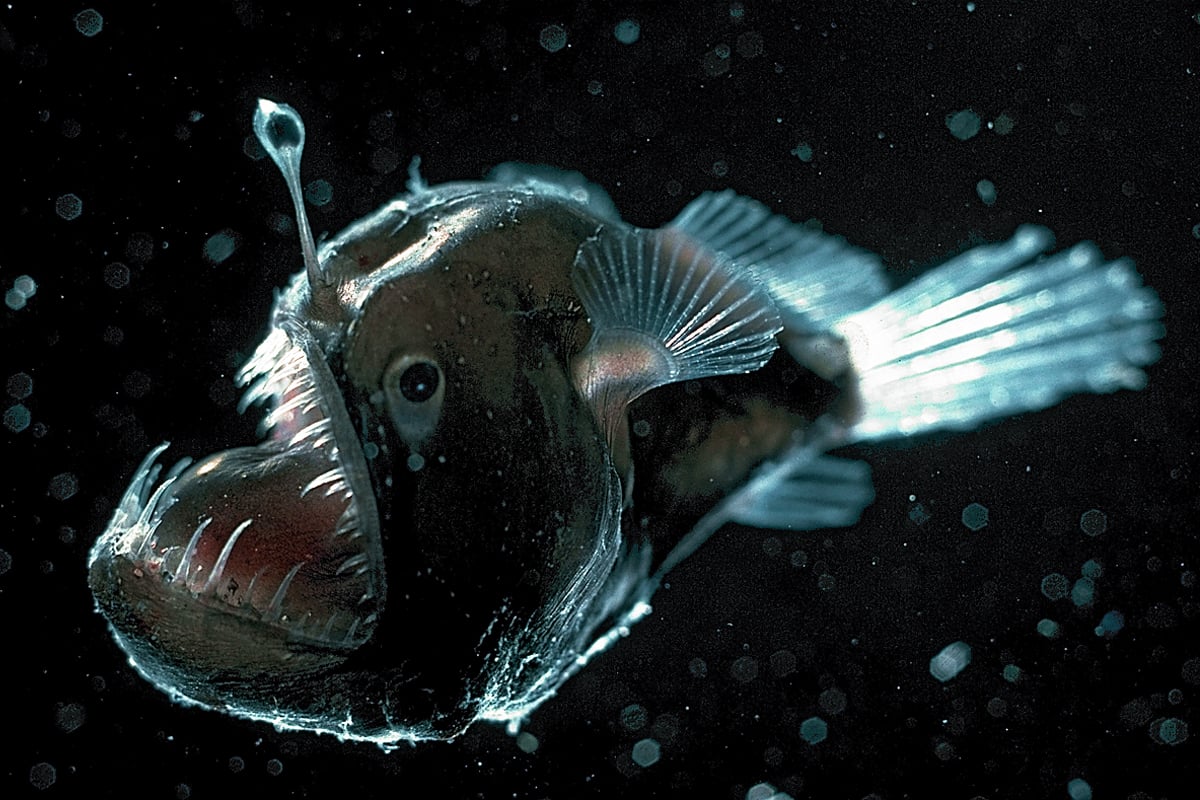
Deep ocean animals adaptations. In anglerfish Linophryne Fig 24 the light is used as a. For example many types of seaweed attach. The photic zone also known as the sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a lake or ocean that receives sufficient sunlight to support aquatic plant life.
In future lessons students will research rocky shore animals to compare animals in these 2 habitats. Watch a recording of this video webinar. Ocean animals have unique adaptations depending on what ocean habitat they.
The dense ocean water is filled with tiny floating organisms. Enzymes exhibit reduced perturbation of function by pressure membranes have fluidities adapted to deep-sea pressures and temperatures and proteins show. Have students identify animal adaptations in.
Encourage students to think about adaptations in marine animals related to obtaining food providing camouflage or safety from predators or dealing with changes in temperature salinity pressure lack of sunlight and need for oxygen. Connection to NGSS -. In some other deep-sea fishes eyes are very small as they are of little apparent use and still others are without eyes.
They have strong shells that protect them from wave action drying out and the prying beaks of predators. Rods help eyes sense light. Some of the most amazing adaptations are from ocean animals like sharks jellies starfish stingrays and dolphins.
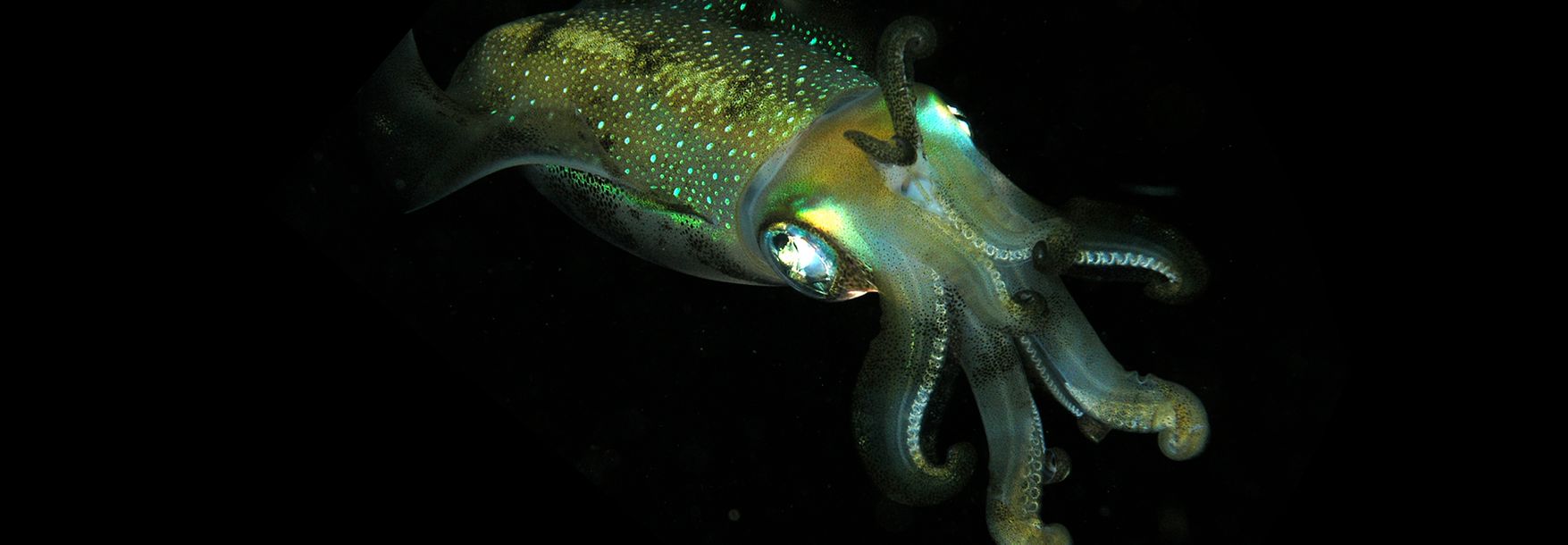
The deep sea is not only under a lot of pressure but it is also very dark. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive. Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive.