Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Glucose and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecule eg.
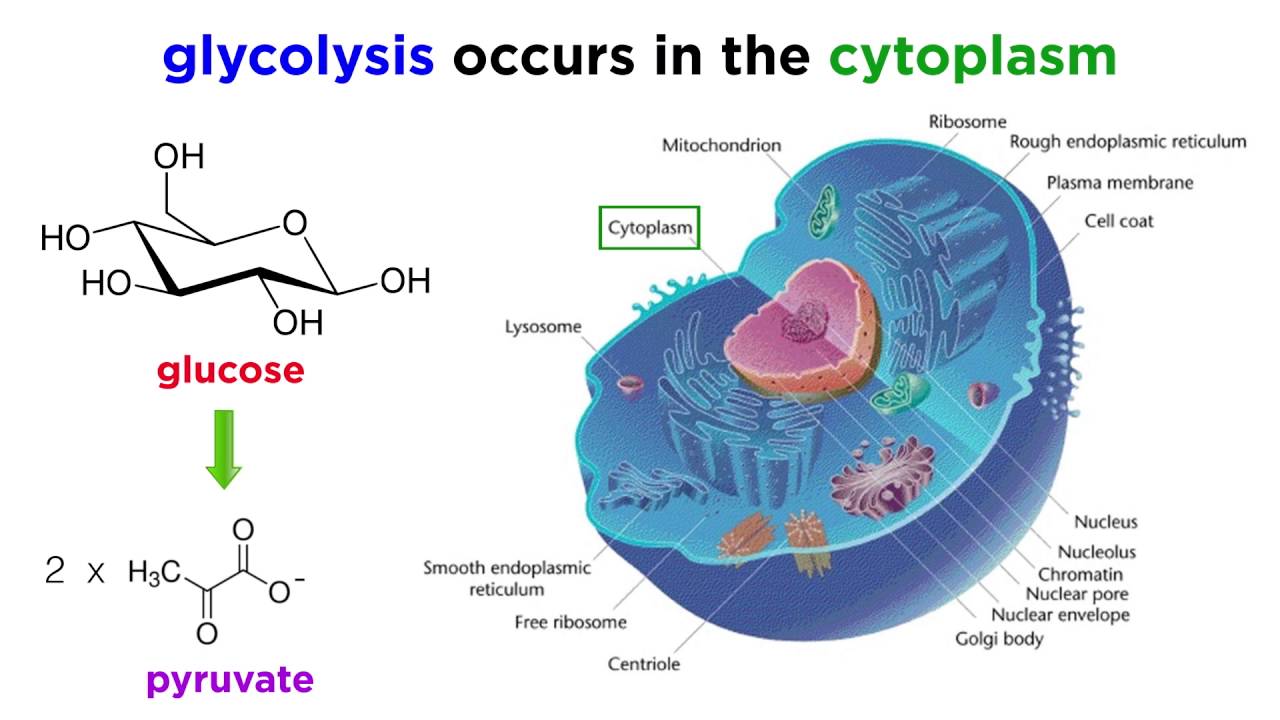
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Where cellular respiration happens. The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules.
Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. ATP for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. Related Biology Terms. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration.