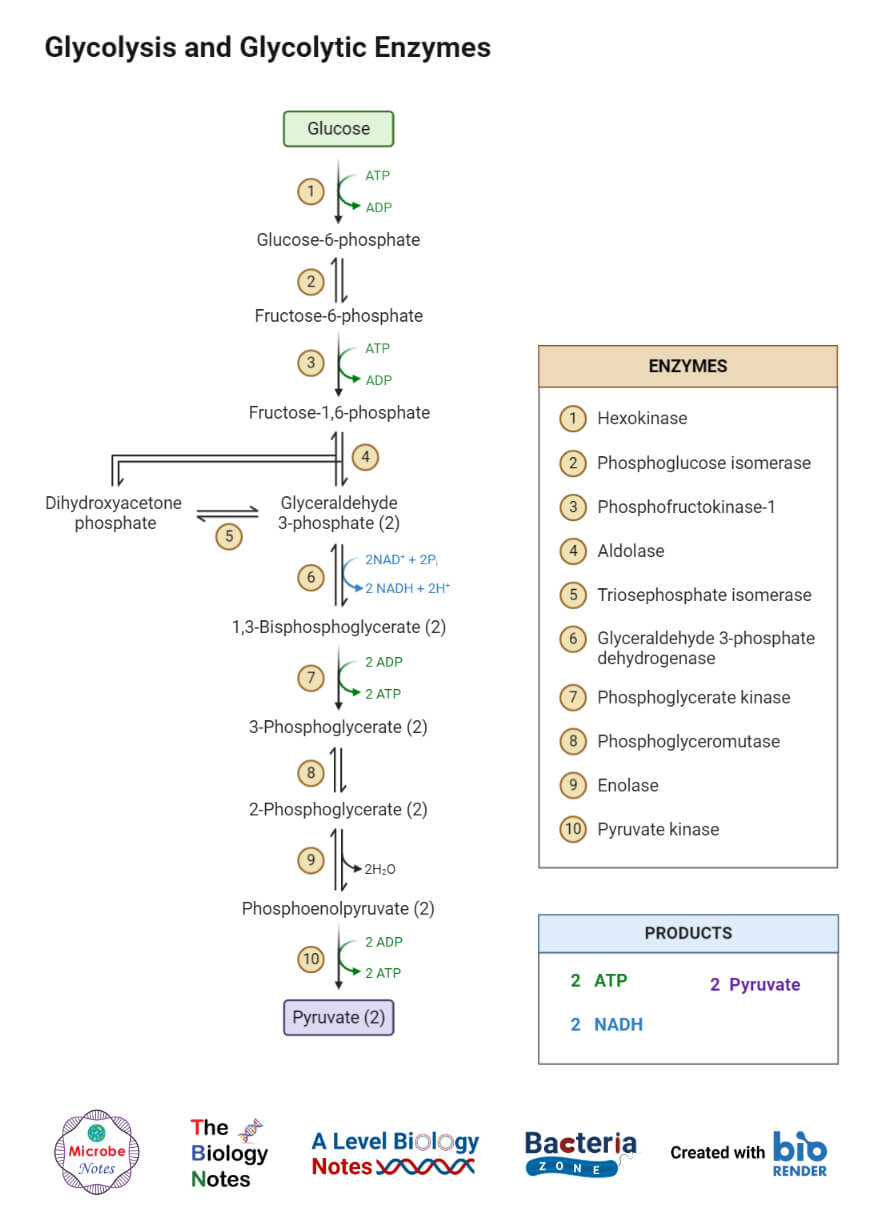
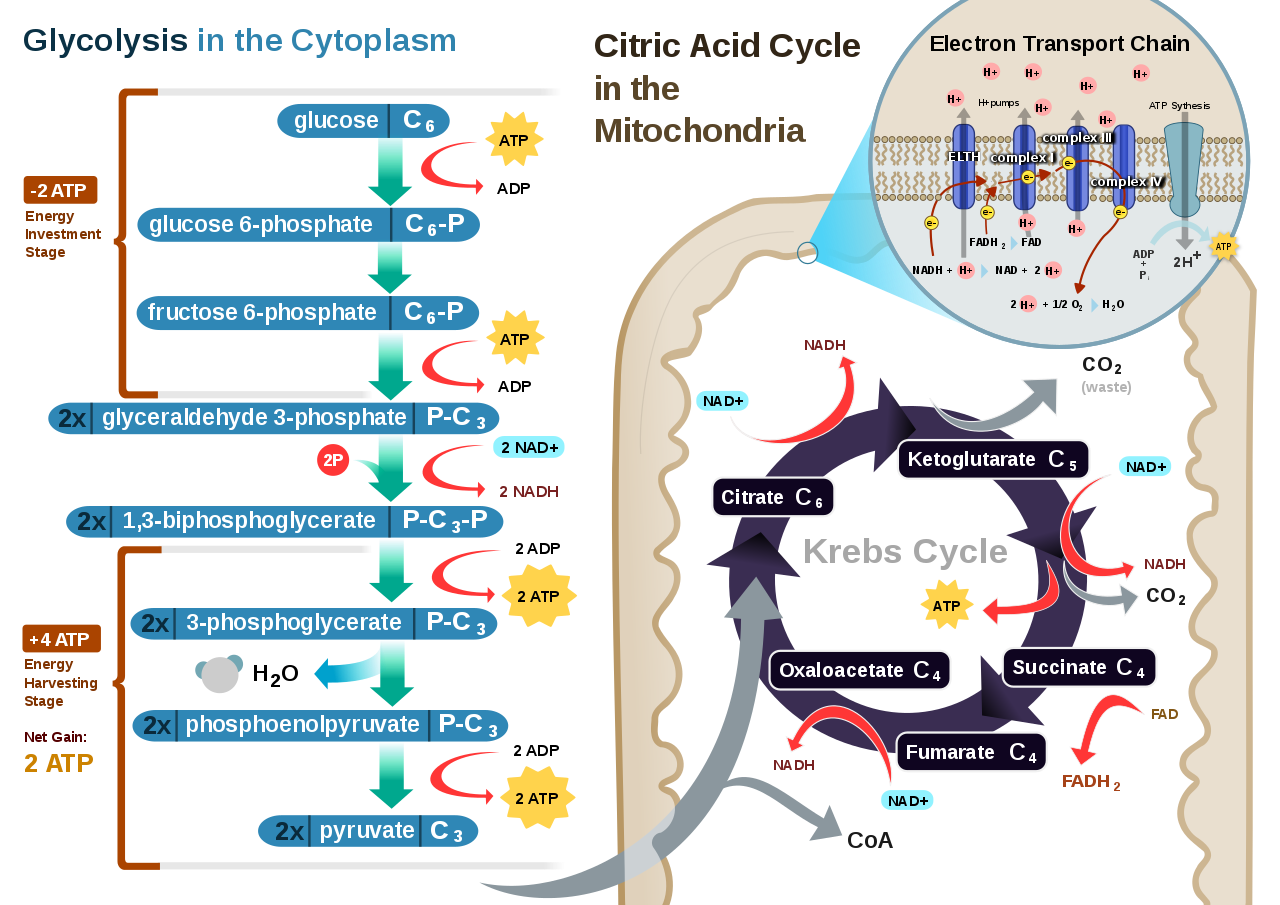
Cellular Respiration Equation Definition

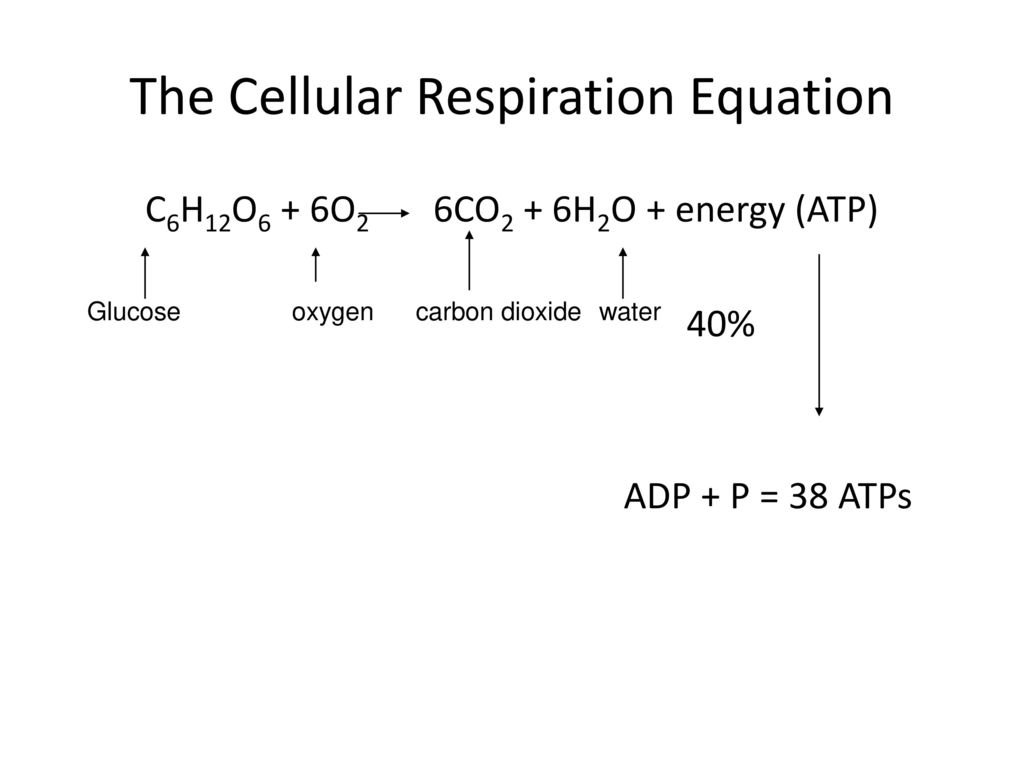
Cellular Respiration aerobic C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O 32 ATP Photosynthesis 6CO2 6H2O C6H12O6 6O2 By looking at the two formulas it becomes evident that the products of one of the reactions are reactants of the other.
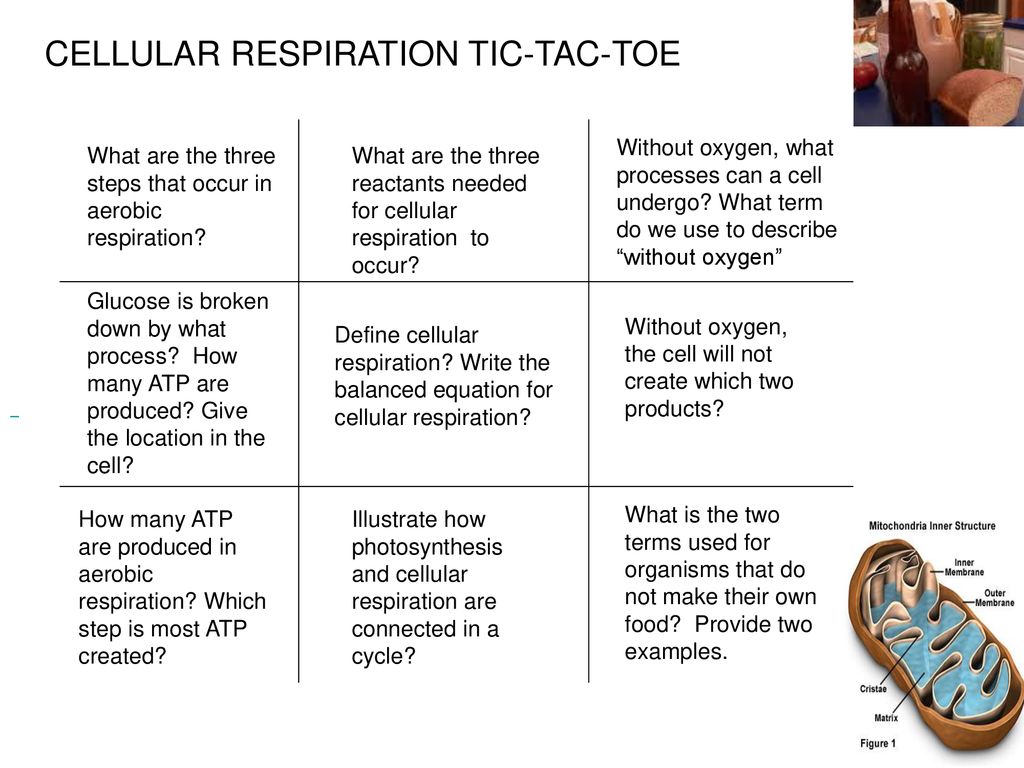
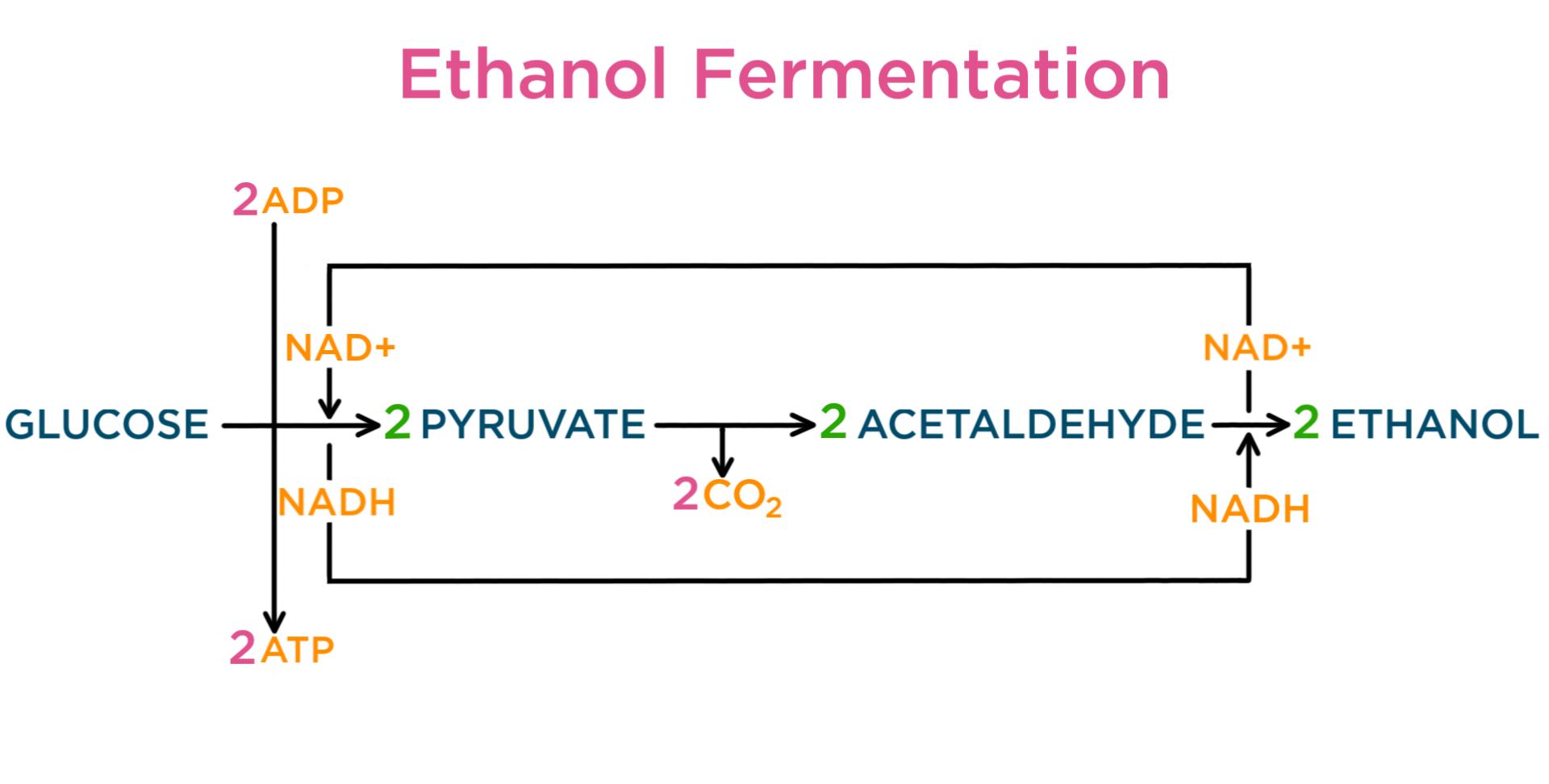
Cellular respiration equation definition. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a metabolic pathway Two types of cellular respiration exist. Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration an equation an output description and an illustration. Aerobic or respiration in the presence of oxygen and anaerobic or respiration without oxygen.
C 6 h 12 o 6 6 o 2 6 co 2 6 h 2 o energy as atp the word equation for this is. The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. It occurs within the cells of all living organisms including both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates. Various sugars amino acids and fatty acids can be used as the substrate for cellular respiration.
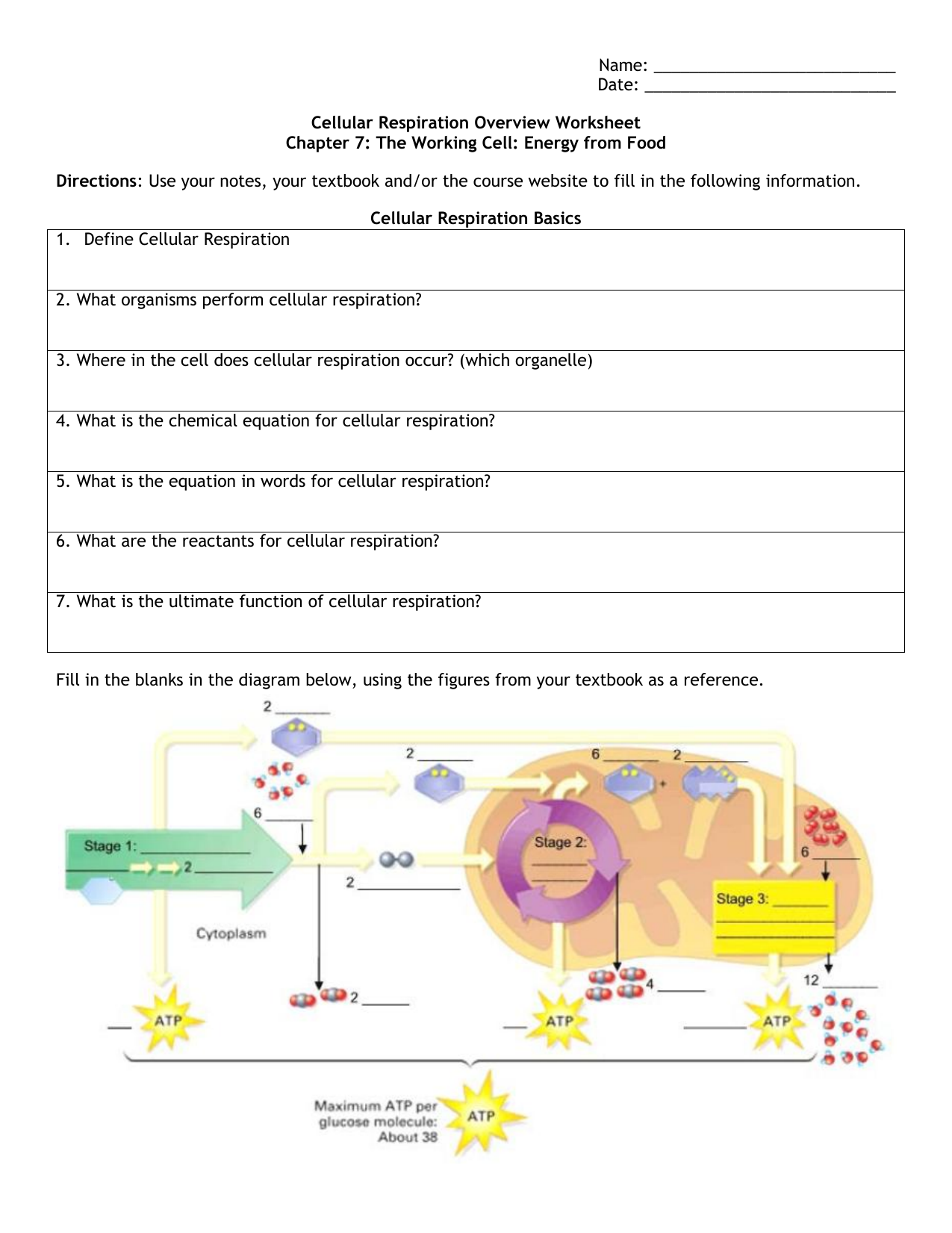
Cellular Respiration Definition. The process takes place in four stages. The chemical formula for the overall process is.
What is Cellular Respiration. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates. Cellular respiration is a set of biochemical reactions that takes place in most cells.
This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals birds humans and other mammals. Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Cellular respiration is the process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy. It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen to produce energy.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)