Cell Membrane Structure Journal

35Q30 92C50 74F10 1.
Cell membrane structure journal. The cell membrane is a complex barrier separating every cell from its external environment. Ad Reveal the Subcellular Localization in Cell Imaging Applications. These proteins have transmembrane domains which insert into the lipid bilayer and can form complexes with both extracellular and intracellular proteins.
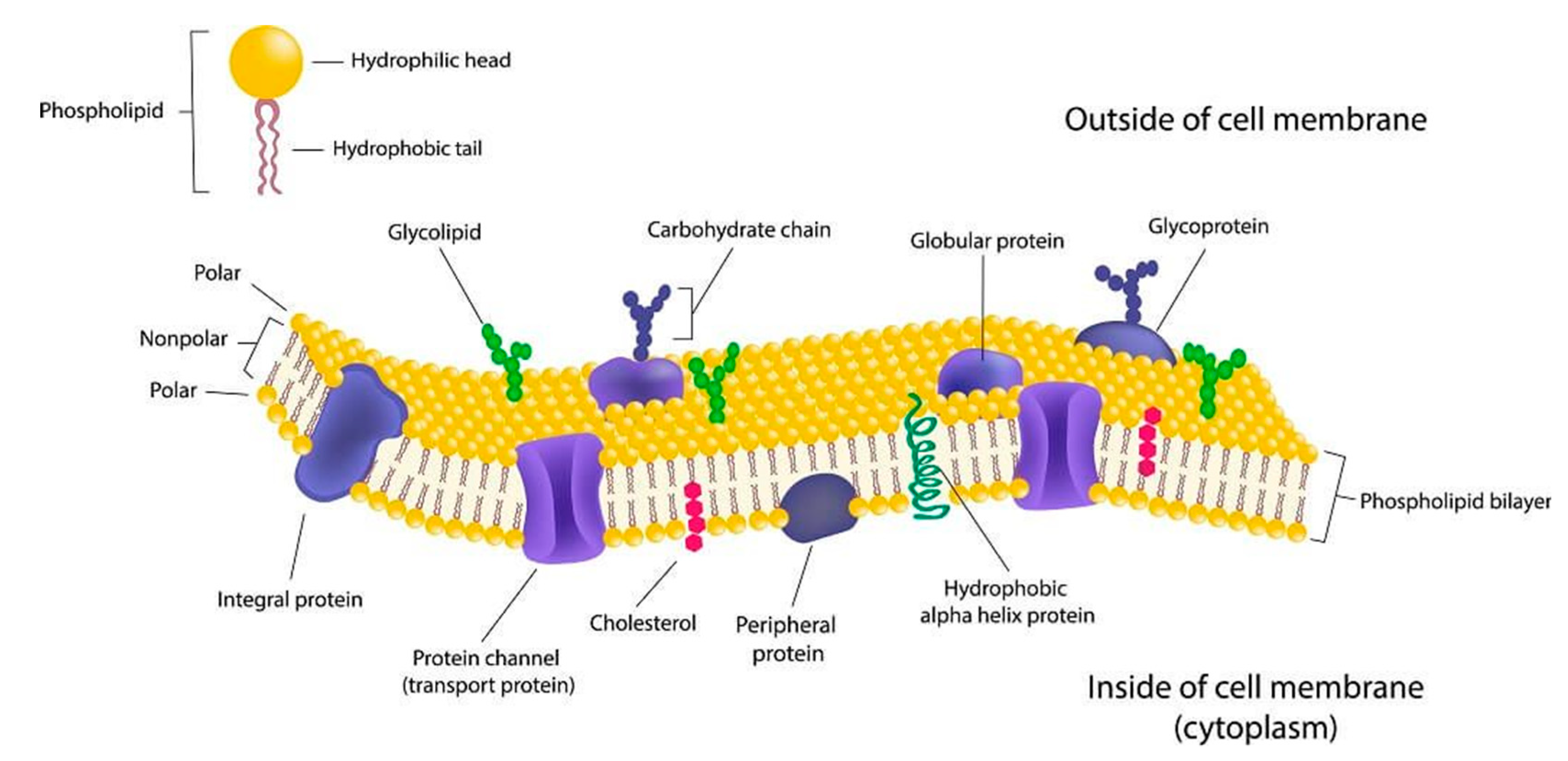
Thefluid mosaic model ofthe cell membrane. The cell membrane is a fluid mosaic of proteins floating in a phospholipid bilayer. 1 15 Amer Assoc Blood Banks Arlington VA 1986 Google Scholar.
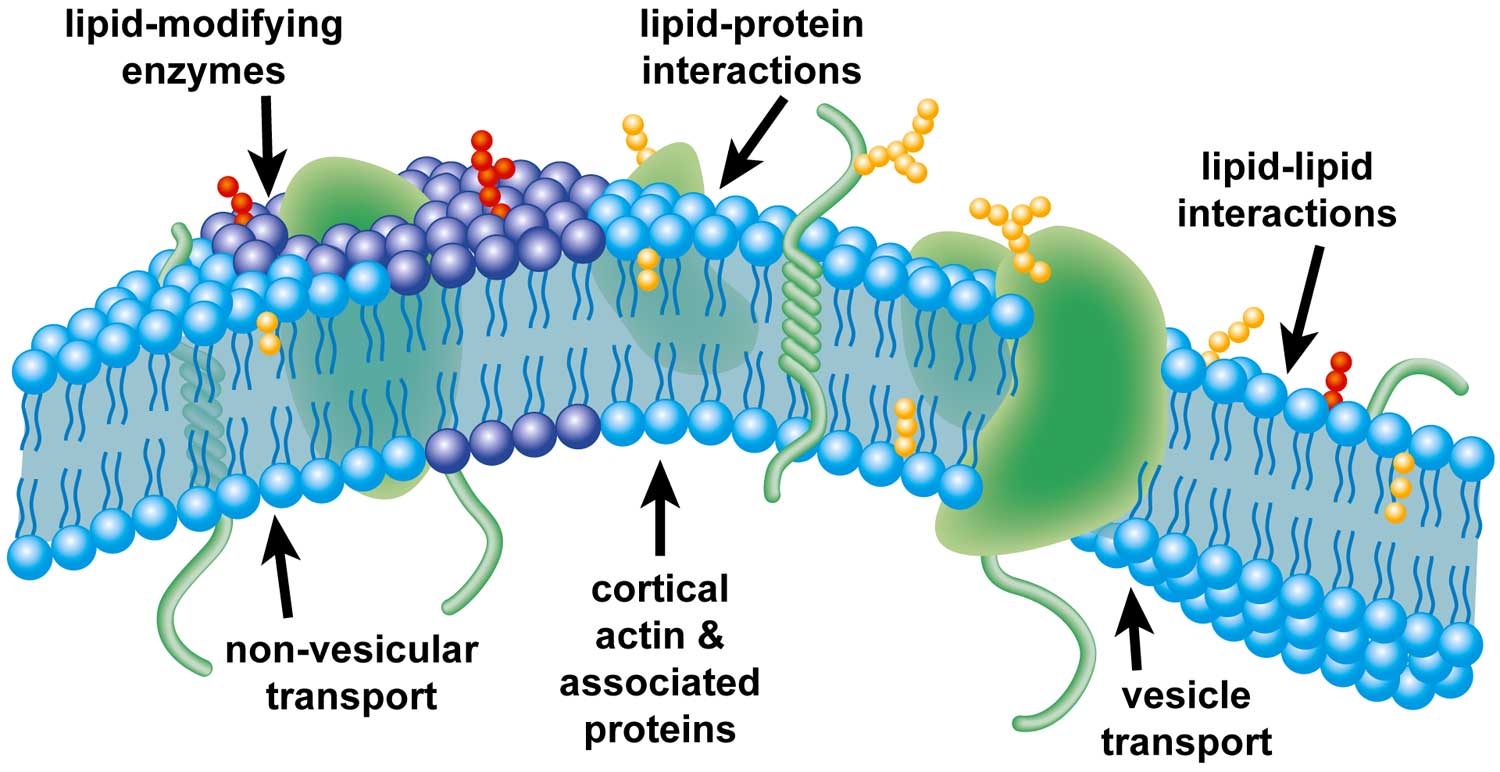
The fascination of membrane research is that the functionality of the cell membrane is dependent on the carefully orchestrated and mutually interdependent properties of lipids and proteins. 3 in Singer S. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane.
THE formation of single stable bimolecular lipid and proteolipid1 membranes up to 10 mm2 in area has been accomplished routinely in 01 M saline solution by methods analogous to the formation of. Garratty G pp. Our editorial process.
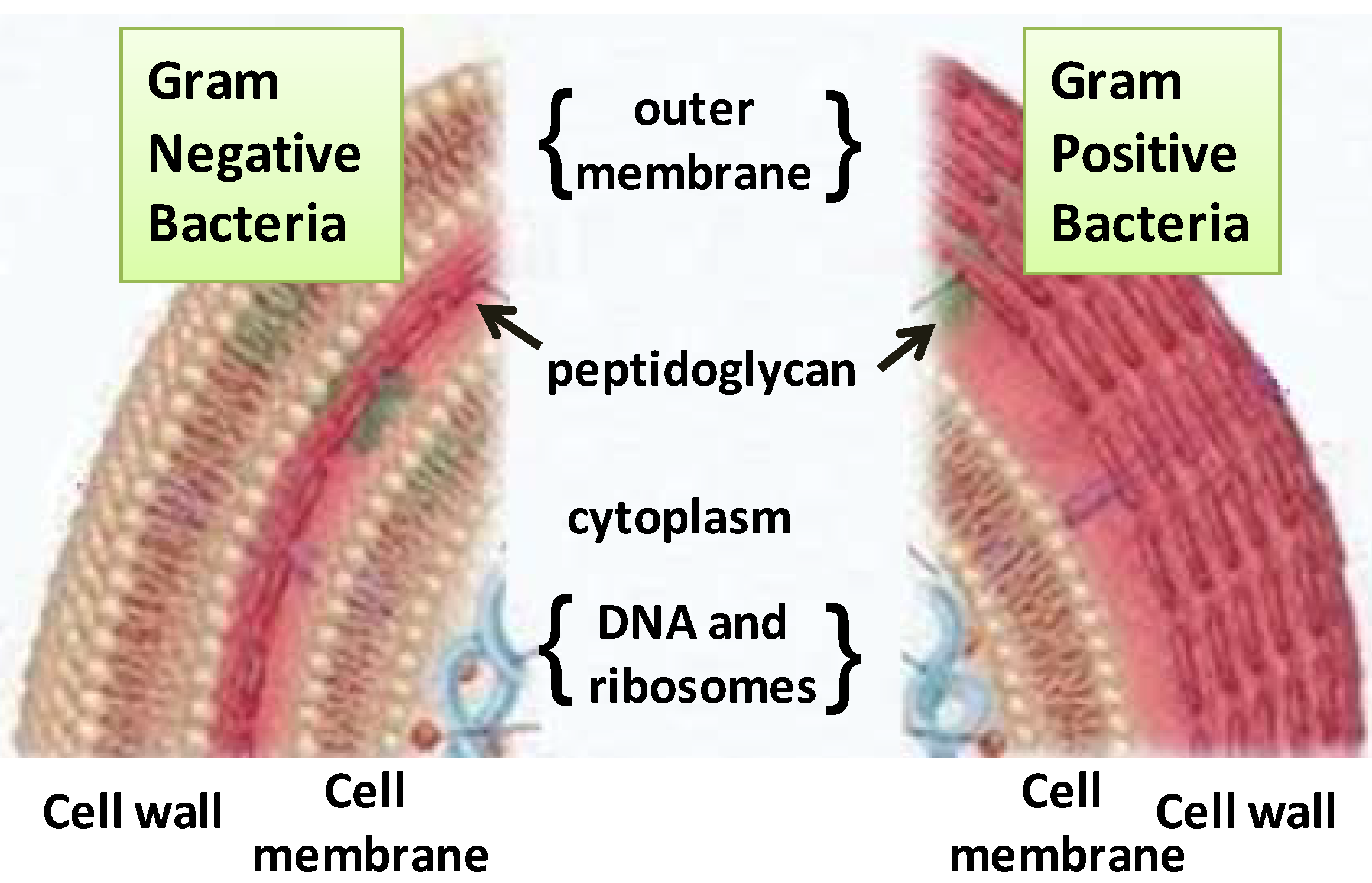
A cell membrane is not a lamellar phase but a real object whose structure corresponds more or less to a lamellar phase. This Selectively Permeable membrane regulates what passes into and out of the cell. Blood group active components of the human red cell membrane.
Recent studies indicate that the cell membrane interacting with its attached cytoskeleton is an important regulator of cell function exerting and responding to forces. Cell membranes are dynamic structures composed of lipid bilayers and integral membrane proteins. Transmembrane Peptides as Sensors of the Membrane Physical State.